Ekofisk 2/4 K
- Combined drilling, water injection and accommodation platform
- Installed in 1986
- Operational in 1987, with water injection starting on 28 December 1987
- Also known as Ekofisk Kilo
 Ekofisk 2/4 K, bro,
Ekofisk 2/4 K, bro,Its accommodation module provides 182 beds over six stories. Standing three kilometres north of the Ekofisk Complex, 2/4 K is connected to the adjacent Ekofisk 2/4 B platform by a bridge. Flying time from the complex is two-three minutes.
While construction of the various platform components was in full swing, the Dyvi Beta jack-up drilling rig was positioned alongside 2/4 B to predrill as many injection wells as possible.
The platform jacket (support structure) was fabricated at Aker Verdal north of Trondheim, while Haugesund Mekaniske Verksted near Stavanger produced the module support frame (MSF). DB 102, the world’s largest crane ship, carried out offshore installation.
 historie, 1996, forsidebilde, kjemikalier lekker ut i havet,
historie, 1996, forsidebilde, kjemikalier lekker ut i havet,Waterflooding is used to improve oil and gas recovery, providing pressure support by replacing the hydrocarbons as they are produced. The water injected must undergo an extensive process of filtration and addition of specific chemicals.
Representing a new generation of platforms on Ekofisk, 2/4 K is equipped with the latest technology – computers and digitalisation have been adopted to a greater extent than on the older platforms in the Greater Ekofisk Area.
Water has also been supplied by 2/4 K to the Ekofisk 2/4 W platform since 1990 for pressure maintenance in the southern part of the reservoir. Additional injection water has later been supplied to 2/4 K from Eldfisk 2/7 E.
Two derricks were installed on 2/4 K. The main one, rig 48, drills to the top of the reservoir, when the smaller rig 50 takes over to drill through the formation and complete the well.
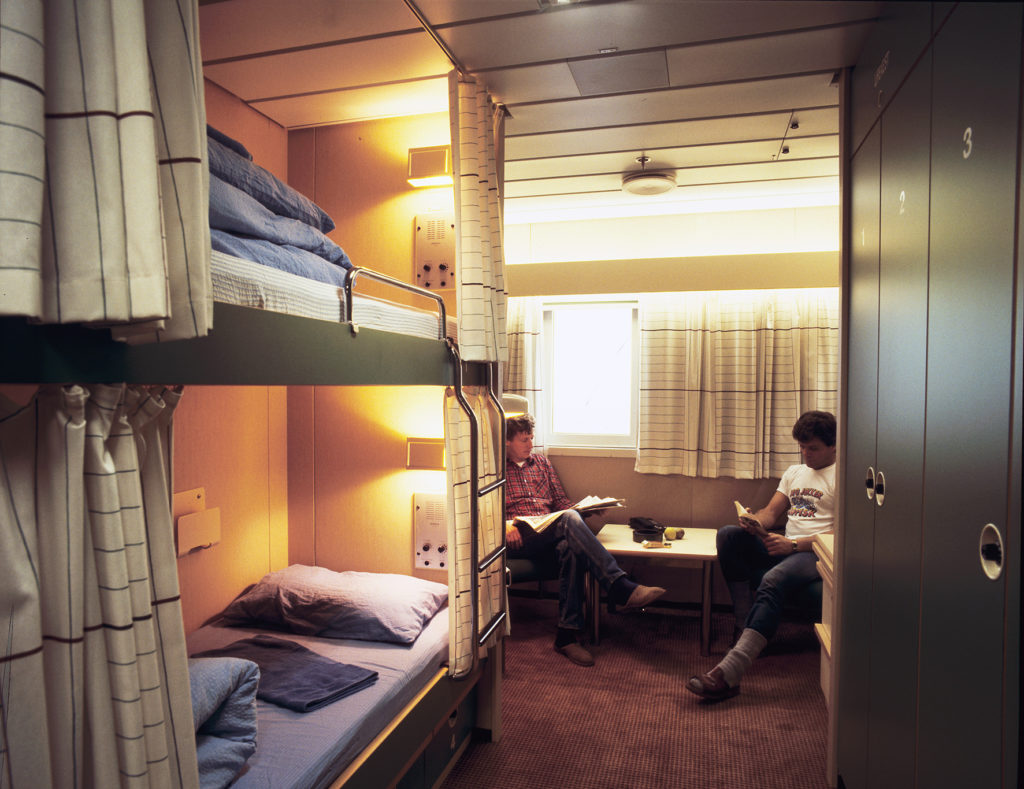 Ekofisk 2/4 K, fritid,
Ekofisk 2/4 K, fritid,Since 2/4 K is tied to 2/4 B by a bridge, it was provided with a large and modern accommodation module which also accommodates workers on the latter installation.
Control functions on 2/4 B were transferred in 1995 to 2/4 K, which means that the control room on the latter could operate both platforms.
Remote monitoring of Edda 2/7 C and Albuskjell 1/6 A was taken over by 2/4 K in mid-May 1999. These installations then shut down and, rather than leaving them staffed until the wells were permanently plugged, a solution was introduced based on remote operation of such functions as emergency shutdown, fire and gas systems, ventilation, power supply and well status.






